What is CMMS?
A Computer Maintenance Management System (CMMS) is a software solution designed to help organizations simplify and facilitate maintenance management operations. CMMS is described in several ways: Computerized Maintenance Management System (CMMI); CMMS software; CMMS System; CMMS platform; or simply maintenance software.
CMMS is an advanced digital platform that serves as a centralized database to manage, monitor and analyze the various elements of an operation, including inventory planning, tracking, and labor organization and equipment maintenance.
Optimizing maintenance procedures, prolonging asset life, reducing operating expenses, and improving regulatory compliance are some of the main objectives of a CMMs in an organization. CMMS helps maintenance teams work more efficiently by centralizing data and automating maintenance management tasks. The fundamental component of a CMMS is your database. This releases resources for strategic initiatives and preventive maintenance instead of being consumed by manual and intensive work operations.
How does a CMMS work?
The main objective of a Computerized Maintenance Management System (CMMS) is to increase the visibility of maintenance management for teams and, as a result, improve the efficiency of an organization.
CMMS helps improve in various areas, including:
 Data Centralization: Fundamentally, CMMS establishes a single centralized database for assets, equipment, inventory and maintenance procedures. Work orders, maintenance schedules, location, warranty details, inventory, assets, equipment and maintenance data can be included in a centralized database. Organizations can eliminate data silos through broad access of the team to the software platform, offering permissions according to staff needs. This allows the correct level of access to information for all stakeholders who need to make informed decisions, establishing a single real source.
Data Centralization: Fundamentally, CMMS establishes a single centralized database for assets, equipment, inventory and maintenance procedures. Work orders, maintenance schedules, location, warranty details, inventory, assets, equipment and maintenance data can be included in a centralized database. Organizations can eliminate data silos through broad access of the team to the software platform, offering permissions according to staff needs. This allows the correct level of access to information for all stakeholders who need to make informed decisions, establishing a single real source.
Maintenance Scheduling and Planning: Proper planning and scheduling of preventive and corrective maintenance tasks are improved by CMMS. Preventive maintenance operations are scheduled based on predetermined intervals or triggers of use to maintain regular maintenance of assets and reduce the risk of non -planned assets failures. Corrective maintenance is also used to deal with any unforeseen problem. Based on these schedules, the system can automatically create work orders, ensuring that maintenance tasks are completed in time and that resources are correctly optimized.
Materials Management and Inventory: The inventory of replacement parts and supplies needed for maintenance work is managed by CMMS. It defines refueling points, automates the purchase process and monitors inventory levels. In addition to reducing inactivity time and unnecessary inventory maintenance costs, effective inventory management ensures that parts are available when necessary.
Service Orders Management : When preventive or corrective maintenance is required, CMMS facilitates the creation of work orders. These work orders specify tasks, necessary resources, equipment and parts, and assigned workers. The workflow and prioritization of tasks are improved when maintenance staff receive notifications and can update the status of work orders in real time.
Reports and Analysis: Comprehensive reporting and analysis tools that provide insights on asset performance and maintenance operations are provided by CMMS. Organizations can generate reports on various parameters, including maintenance costs, inactivity time, asset life, and schedule compliance. These insights help in identifying trends, decision making, and continuous improvement of maintenance strategies.
Mobile Accessibility and Integration: Mobile accessibility of many modern CMMS solutions allows the maintenance team to use mobile devices to access the system, check work orders, and change task status from anywhere. CMMS can also be integrated into other systems to improve operational efficiency and data transmission, including Business Resource Planning Systems (ERP).
What are the benefits of CMMS?
CMMS provides crucial features and benefits in various industries, such as oil and gas production, mining, sanitation, power generation, manufacturing, data centers and other critical active industries. These benefits are evident in increasing asset life and performance and extending to enable maintenance teams with resources to work more efficiently.
CMMS Benefits for Assets
Enhanced Reliability of Assets: Organizations can change reactive methods to proactive maintenance methods such as CTM technology, with the help of a CMMS. The transition from manual approaches to a digital platform results in more reliable assets by reducing the frequency of unproversed equipment failures.
Extending Asset Life : The operational life of assets is greatly increased through better management of assets on a software platform. CMMS allows better schedule and more timely repairs. Organizations can improve capital spending by avoiding early substitution costs and ensuring equipment operating within their ideal parameters.
Enhanced Performance and Efficiency: Ensuring the ideal efficiency of assets is achieved through continuous monitoring and maintenance. This increases activity time and quality while reducing operating costs and energy consumption, increasing productivity and margins of the organization.
Compliance and Safety: Performing maintenance tasks that follow security procedures prescribed within strict legal requirements is facilitated using a CMMS. This ensures a safer work environment for employees and compliance with industry guidelines, reducing the likelihood of accidents and costly fines.
CMMS Benefits for the Maintenance Team
Data Decision Making: CMMS Software uses reports and data analysis to provide insightful data for the most appropriate action taking. This data can help maintenance managers identify trends, predict subsequent requirements, allocate resources more efficiently, and decide on investments in assets and maintenance approaches.
 Workflow and Simplified Operations: The paperwork can be eliminated and administrative responsibilities reduced with a CMMs, centralizing information and automating task schedule and allocation. Access to work orders, schedules and real -time data from anywhere improves the efficiency and collaboration of maintenance teams. Features can be efficiently allocated by using CMMS, helping the maintenance team prioritize tasks, ensuring the opportune completion of optimized maintenance activities.
Workflow and Simplified Operations: The paperwork can be eliminated and administrative responsibilities reduced with a CMMs, centralizing information and automating task schedule and allocation. Access to work orders, schedules and real -time data from anywhere improves the efficiency and collaboration of maintenance teams. Features can be efficiently allocated by using CMMS, helping the maintenance team prioritize tasks, ensuring the opportune completion of optimized maintenance activities.
Increased productivity: Maintenance personnel can focus on more critical and challenging maintenance tasks, automating repetitive operations such as working orders and component inventory management. In addition to increasing productivity, staff can see job satisfaction increase as a result.
Cost Reduction and Budget Management: Organizations can monitor and control maintenance spending more efficiently using a CMMS, which offers accurate records of maintenance activities, costs and asset history. Change to a predictive maintenance model can also reduce the need for emergency repairs, thus reducing costs.
Inventory Management: Maintenance operations depend on accurate data and proper inventory management and replacement components. Part availability is guaranteed by inventory management tools in CMMS software. This also helps in tracking inventory levels by location, serial number, and rehabory management.
The role of CMMS in monitoring based on conditions
Real -time data collection and analysis: Condition -based monitoring is facilitated by CMMS, making it easier to collect and evaluate real time data from the equipment. Sensors or data from controllers can inform various conditions of assets, including vibration, temperature and current flow, and send the information to CMMS. This allows maintenance teams to regularly evaluate the state of assets and identify early warning signs of imminent failures before they occur.
Predictive Maintenance Schedule : Using the data collected, CMMS can predict when the maintenance of electrical assets should be performed. Predictive maintenance scheduling ensures that repairs are done only when necessary, based on maintenance schedules under the active conditions of the assets rather than predefined schedules. This improves the distribution of maintenance resources and avoids unexpected inactivity time.
Historical data tracking and trend analysis: historical data tracking over time and trends analysis are made possible by monitoring based on conditions through CMMS. This provides insights on the performance and useful life of long -term assets, helping to identify anomalies and deterioration patterns. Strategic planning, asset replacement decisions, and optimization of maintenance schedules benefit significantly from this analytical insight.
A computer management system (CMMS) is an essential instrument for future -oriented companies that seek to improve the efficiency, reliability and economy of their maintenance operations and have significant advantages for both maintenance and asset teams. However, CMMS systems still depend on the retroactive analysis of the information collected to make any predictive maintenance decision. That is, there is no automation or added intelligence in the system that allows process automation to avoid breaking or premature wear of the equipment.
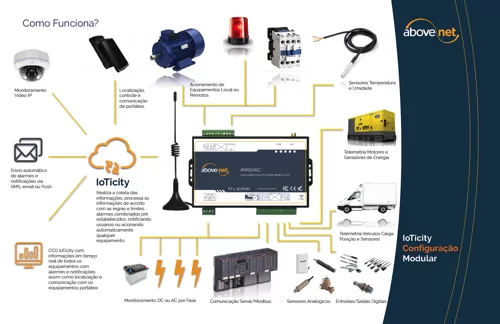
CMMS and IOT Smart
IIOT is transforming various technologies and updating traditional processes of industry, being an ally in improving the concepts of existing systems. In a proactive approach to asset management, unlike traditional supervision systems, we understand that the process cannot only depend on human perception for problem identification. Instead, through smart IoT, it is possible to quickly detect anomalies and, automating processes, send immediate alerts to maintenance teams.

This response capacity allows companies to correct problems before they get worse, avoiding onerous interruptions and damage. This concept is an agent of change in asset monitoring and management, allowing companies of all sectors and sizes to increase efficiency and safety significantly.
The complete parameterization of the intelligence of the operation and the proactivity of alarm with tasks directly to the maintenance and field team are fundamental characteristics. By automating these tasks, the intelligent solution ensures that each anomaly is treated uniquely and effectively, significantly reducing inactivity time and operating costs.
The advantages of this approach include the ability to make faster and more informed decisions, which is essential for maintaining continuous and efficient operations. In addition, it allows companies to move from manual reactive operation to an automated predictive and proactive approach, improving the reliability of assets and the overall efficiency of the operation.
This not only maximizes asset life, but also improves operational safety, ensures regulatory compliance, increases maintenance team productivity, and reduces operating costs.
And there? Do you have a CMMS in your company? Would you like him to be smart?