The increase in hospital fires in Brazil indicates a growing concern about safety in one of the most critical environments for humanity. According to the Sprinkler Brasil Institute, in 2023, 49 cases of fires were recorded, a 16.9% jump in occurrences compared to the previous year.
The data signal an urgent need to review and strengthen protection measures against hospital fires. These incidents not only disrupt vital healthcare services, but also pose an extreme risk to patients and staff.
Recent occurrences illustrate the severity and human impact of these accidents. In one case, the emergency evacuation of an intensive care unit led to the tragic death of an elderly patient , highlighting the vulnerability of individuals who depend on these health services. In another episode, a short circuit in air conditioning equipment caused an intense emission of smoke in a hospital, generating panic and requiring an immediate response from emergency teams to avoid further damage.
These events reinforce the importance of establishing and maintaining effective methods and measures to prevent hospital fires. The difficulty of manual inspection, the lack of knowledge of the status of critical parameters that indicate an ignition and the potential for human error in equipment maintenance, highlight the urgency in adopting intelligent mechanisms and technologies for rapid proactive reactions.
Risk Mitigation by Identification of Critical Points and Boundary Systems
Proactively preventing hospital fires starts with identifying and mitigating risks before they become a real threat. In the event of a fire, we need to make sure that contour systems come into action as they were designed.
Hospital Kitchens
The most common place for hospital fires to start in the world, and in Brazil it is no different, is the kitchen. These environments are considered high-risk areas, and especially in hospitals, due to the restricted mobility of patients, the nature of the equipment and the presence of flammable materials, such as oils and fats.
Exhaust ducts often accumulate grease and oils over time, which can be dangerous. Excessive heating of these pipes can cause ignition, leading to tragic consequences. The fire code requires the installation of a CO2 plant to combat the outbreak of flames. However, it is not uncommon for these plants to fail, whether due to inadequate maintenance, recharging problems or even their non-existence, which is in disagreement with fire department regulations.
 Another common problem is forgetting to turn off equipment at the end of work or activities. Similar to ignition in the exhaust ducts due to excessive temperature in a grill, electric fryers or ovens can also cause fires if left on for an extended period of time.
Another common problem is forgetting to turn off equipment at the end of work or activities. Similar to ignition in the exhaust ducts due to excessive temperature in a grill, electric fryers or ovens can also cause fires if left on for an extended period of time.
The fat that accumulates in hoods and ducts acts as fuel, fueling the ignition and increasing the fire to catastrophic proportions.
In any case, any intervention, whether by the CO2 plant, or by another fire-fighting system such as sprinklers, is a workaround measure for a situation that is avoidable at any cost as it causes large-scale losses with damage to facilities and equipment, interruptions of operation, and eventually patient deaths.
Electrical Boards and Circuits
The second biggest cause of fires is heating of power connections and cables caused by excessive load and poor contact.
Generally, institutions add equipment and relevant consumption to existing facilities and do not bother to carry out a load study or use limit of the installed infrastructure. During the summer, especially in tropical cities, where the ambient temperature exceeds 40ºC, an installation close to its load limit (current) can easily overheat and initiate a short circuit, generally followed by ignition and large fire.
Poor contact between terminals and cables can also lead to fires at peak times of use where the current and demand on the systems are maximum.
The traditional way of preventing electrical panels and circuits is by manual periodic inspection that includes thermography of the circuits. Basically, the technical team uses portable infrared temperature meters to measure the temperature of the bus and cables at the time of inspection. However, this method is not 100% safe as it only provides a sample of the state of the buses at a certain time of the day, which does not necessarily represent peak usage.
In other words, it is not uncommon for fires to occur even with manual thermography procedures up to date.
If the fire was inevitable, it must be controlled
Another major problem is the proper functioning of fire control systems.
CO2 and FM automatic fire extinguishers
During an event, automatic CO2 or FM gas extinguishing systems can be activated automatically to put out a fire. However, because these systems are never used, they are often unloaded or closed, without the proper knowledge of the establishment's operational team. During an emergency, trigger failure can transform a small event into a major one.
Sprinkler Systems
Depending on the type of installation, sprinkler systems, also with automatic activation, are mandatory. However, for its proper functioning during a fire outbreak, correct pressurization of the fire fighting system (SCI) is necessary. If the network is not properly pressurized and the pumps are ready for use, the sprinkler system will not be able to overcome the initial fire.
Similar to automatic fire extinguishing systems, these systems also run the risk of being closed or with the automatic pumps turned off, preventing them from being activated during the emergency.
Water reserves
Another extremely important item is the reserve of water for fires. Buildings and commercial establishments need to have a water reserve for firefighting. This reserve is guaranteed by a differential in the water tank outlet level, where the shallowest is for normal supply and the deepest is for the fire reserve. Due to terrible coincidences, and due to human error in maintenance, often during the washing or maintenance of the boxes, establishments are left without the minimum water level or do not adjust the minimum level of the box after washing, leaving the level below the minimum reserve for a period of time. supply shortages.
Generators
Generators are essential for the continuity of operations in hospitals, especially during a fire that can cause interruptions by the utility company. Energy is essential to activate fire fighting systems and especially water pumps.
This equipment depends on several factors such as fuel, batteries in good condition for starting, oil quality, among others that can prevent the generator from starting at a crucial moment. Preventive maintenance may not be enough to guarantee its operation and power failure becomes a decisive factor between the life and death of patients.
With so many risks, how can we avoid these events?
There is only one way to prevent and anticipate these events: Constant information on the status of all critical installations. Several studies in hospitals indicate that standardizing communication and increasing process surveillance reduces the incidence of errors and increases reliability and safety, whatever the process.
The big problem is what to do to implement 24x7 surveillance of so much physically separated equipment, with different technical characteristics that require specific knowledge of energy, generation, hydraulics, gases, etc.
Unfortunately, it is economically unfeasible to relocate or deploy on-call teams for continuous inspection of each of these subsystems.
The solution is then continuous monitoring in order to send alerts to the maintenance team.
Bridgemeter Intelligent Infrastructure Monitoring
The Bridgemeter platform exemplifies innovation in this area, offering connection capabilities and continuous monitoring for any type of equipment or sensor. This tool is vital in hospital environments, where equipment failures can have serious consequences.
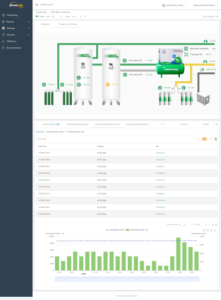
Critical variables such as load and consumption, bus temperature, tank and line pressures, and operational status of equipment are continuously monitored. This data is analyzed in real time to identify any deviations that could indicate a fire-prone condition.
Predictive analytics uses performance data to identify patterns and trends that suggest the need for predictive maintenance. Alerts enable proactive interventions, minimizing the risk of fires caused by overload or system defects.
In addition to improving safety, these proactive interventions contribute to extending the useful life of equipment and increasing the operational efficiency of hospitals. Maintenance, driven by predictive data, not only guarantees a safer environment, but also optimizes the use of resources and reduces costs with failures and emergency repairs.
Monitoring in Hospital Kitchens
Several parameters can be monitored in a hospital kitchen to ensure its proper functioning:
- Hood Temperature: Whether by temperature of the ducts or the preparation surface through infrared, the system detects temperatures outside considerable limits
- Condition of equipment: Fryers, ovens or any other equipment that has an on/off switch can serve as an information base for risk assessment.
- Level of grease encrustation in ducts: A very important factor that may indicate the need for cleaning, eliminating one of the main fuels and fire intensifiers in kitchens.
Monitoring of Electrical Panels and Circuits
Through continuous monitoring of bus temperature at strategic points, it is possible to safely assess the network usage limit even in adverse conditions such as summer days and electrical system overload. The Bridgemeter identifies the temperature trend of the busbars and can indicate the need to relocate equipment before this heating causes a short circuit. The constant occurrence of heating may indicate bad contacts or the need to resize the panel.
Monitoring of Fire Fighting Systems
The system monitors the operation of the sprinklers, checking water pressures and the tightness of the line, in addition to evaluating the status of the water pumps and identifying leaks, all essential for maintaining the necessary pressure in the system. This data is crucial to keeping the firefighting system ready for immediate use.
In addition, Bridgemeter monitors the levels of water tanks intended for firefighting, ensuring there is sufficient volume for an effective response. Automatic alerts inform the technical team of any deviations, allowing quick and efficient corrective actions.
This integrated monitoring significantly increases safety by ensuring that all elements of the firefighting system function correctly when needed most.
Generator Monitoring
Above-Net 's Bridgemeter ensures efficient operation of generators Bridgemeter also fuel, battery and oil quality levels.
Conclusion
Integrating Bridgemeter into a hospital's infrastructure not only represents a boost in fire safety, but also a significant improvement in operational efficiency and a substantial cost reduction.
Above-Net 's IIoT solution redefines the monitoring of hospital environments, providing a layer of predictive intelligence with security and effectiveness.
This approach not only preserves lives, but also safeguards valuable hospital resources, ensuring the continued delivery of essential health services to the community.
By implementing Bridgemeter , hospitals not only mitigate risks but also strengthen their ability to quickly respond to emergencies, thereby promoting a safer and more resilient environment for patients, staff and visitors.

Catalog
Do you want to know more about how to carry out Intelligent Management of Hospital Infrastructure?
Then download our catalog to explore how IoT monitoring of Hospital Infrastructure improves patient care. Discover intelligent preventative monitoring solutions with Bridgemeter .



