Discover how intelligent generator set monitoring prevents critical failures, reduces costs and ensures the reliability of your energy backup.
It was a typical night on duty at a large hospital when the unexpected happened: a total blackout in the region. In a matter of seconds, all the lights went out. This was exactly the time for which the generator set had been installed. However, when most needed, the equipment remained silent.
In the ICU, doctors and nurses rushed to keep vital equipment running on emergency batteries, while technicians discovered, too late, that the fuel tank was practically empty – a situation avoidable with an adequate monitoring system.
This story, unfortunately, illustrates the risks of operating without an intelligent, predictive monitoring solution. With Bridgemeter , the hospital could have identified and corrected the supply problem early, ensuring continuity of essential care and protecting lives.
This scenario, unfortunately, is not fictional. It occurs with alarming frequency in installations that rely on generator sets as a backup system. Studies in the USA indicate a failure rate of 3% to 4% in these equipment – a seemingly small percentage, but with potentially catastrophic consequences.
In critical environments such as hospitals, industries, data centers and large commercial buildings, continuity of power supply is not just a convenience, but a vital necessity. A single minute of interruption can generate significant financial losses, compromise essential operations and, in the worst case scenario, put lives at risk.
The great challenge of generator sets lies precisely in the nature of their operation: unlike other critical equipment, which works continuously, generators remain inactive until they are indispensable. They are like emergency parachutes – they need to work perfectly the first and only time they are deployed.
The Invisible Risks
In January 2024, a hospital in São Paulo experienced moments of panic when it needed to evacuate its ICU after a fire broke out. In another even more serious case, a hospital in Rio de Janeiro faced tragedy when a fire started in a generator resulted in 14 deaths and 97 injuries. These are not isolated cases — they are dramatic warnings about the risks hidden in seemingly safe equipment.
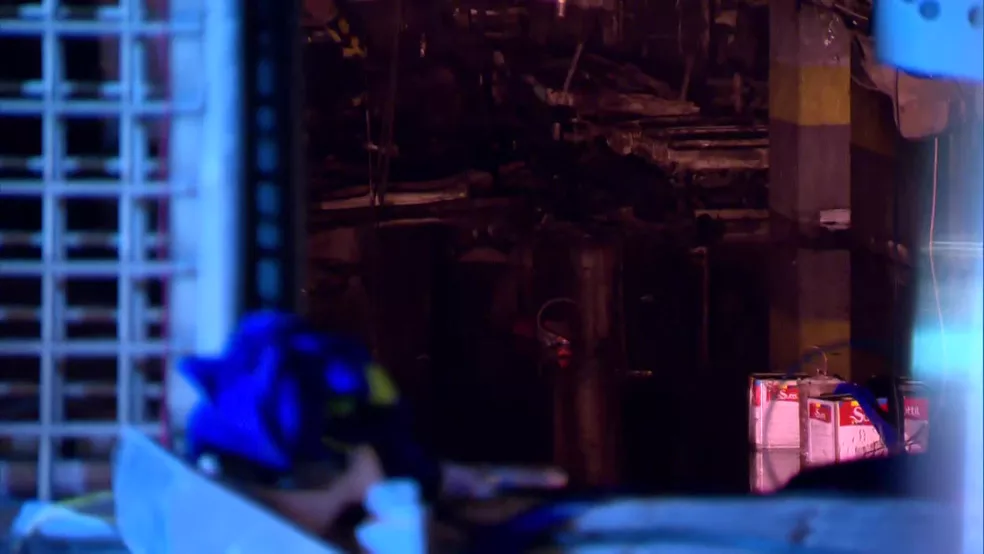

In data centers, where every second of inactivity can cost thousands of reais, the failure of a generator means more than financial losses: it represents the interruption of essential services that affect thousands of users. In industry, an unscheduled stoppage can lead to the loss of entire production batches, damage to sensitive equipment and, in some cases, even risks to the safety of workers.
The False Sense of Security of Traditional Maintenance
The traditional approach to generator set maintenance can be compared to taking a monthly snapshot of something that changes by the minute. During periodic inspections, technicians check fuel levels, test batteries and perform standardized procedures. The generator is turned on for a few minutes, data is collected, and everything appears to be working perfectly. However, the next day, everything may be different.
“It's surprising how seemingly simple situations can compromise an entire backup system,” comments an engineer with two decades of experience in the sector. “I have seen cases where someone needed to start a truck and temporarily removed the battery from the generator. When replacing it, a poor connection compromised the system. In another situation, employees used fuel from the generator for other purposes, leaving the tank dangerously low.”
These inspections cover only 1% of the total operational time, leaving the actual condition of the equipment unknown for the other 99% of the time. It's like driving a car whose instrument panel only works for 15 minutes a day.
In summary, limitations of traditional maintenance include:
- Insufficient temporal coverage : Periodic inspections cover less than 1% of operational time, leaving equipment unattended 99% of the time.
- Excessive dependence on human intervention : subject to errors and a limited view of the inspection range.
- Lack of continuous detection : Problems that arise between inspections can go unnoticed until the critical moment.
- High costs : frequent trips for routine checks represent significant expenses.
- Lack of predictability : inability to anticipate failures before they occur.
- Lack of real-time monitoring : critical parameters are only checked during inspections.
- Difficulty in historical recording : lack of continuous data for trend analysis.
- Reactive response : problems are only identified after they occur.
- Inefficient maintenance : fixed maintenance intervals do not always correspond to the actual use of the equipment.
The Smart Monitoring Revolution with Bridgemeter
It was to face these challenges that Above-Net developed Bridgemeter , a solution that transforms the way we monitor and manage any equipment, especially generator sets. More than a monitoring system, Bridgemeter acts as a tireless guardian, overseeing every aspect of equipment 24/7.
The system operates on multiple layers of protection. At the most basic layer, it continuously monitors critical parameters such as fuel levels, battery status, engine and oil temperatures, pressures and electrical data. However, it is at the intelligence layer that Bridgemeter really shines.
Imagine, for example, a sudden drop in the fuel level during the night, without the generator having been activated. Within seconds, the system identifies anomalous behavior and notifies the responsible team through the Bridgemeter APP mobile, issuing alerts of a possible fuel leak or theft, preventing a possible future crisis. Likewise, subtle patterns of battery degradation, imperceptible in conventional testing, are detected and reported before they cause failure.
Bridgemeter enables real-time monitoring of the following critical parameters:
Engine Monitoring :
- Engine and oil temperature
- Oil pressure
- Engine RPM
- Hour meter
- Cooling system
- Oil quality
Electrical Monitoring :
- Voltage
- Current
- Frequency
- Active and reactive power
- power factor
Resource Monitoring :
- Fuel level and consumption
- Battery status and charge
- Load and usage demand
- Estimated autonomy
- Average consumption
Environmental Monitoring :
- Ambient temperature
- Smoke detection
- Leak sensors
- Ventilation
Bridgemeter offers continuous and intelligent supervision, allowing you to anticipate problems and significantly increase the security and reliability of backup systems.
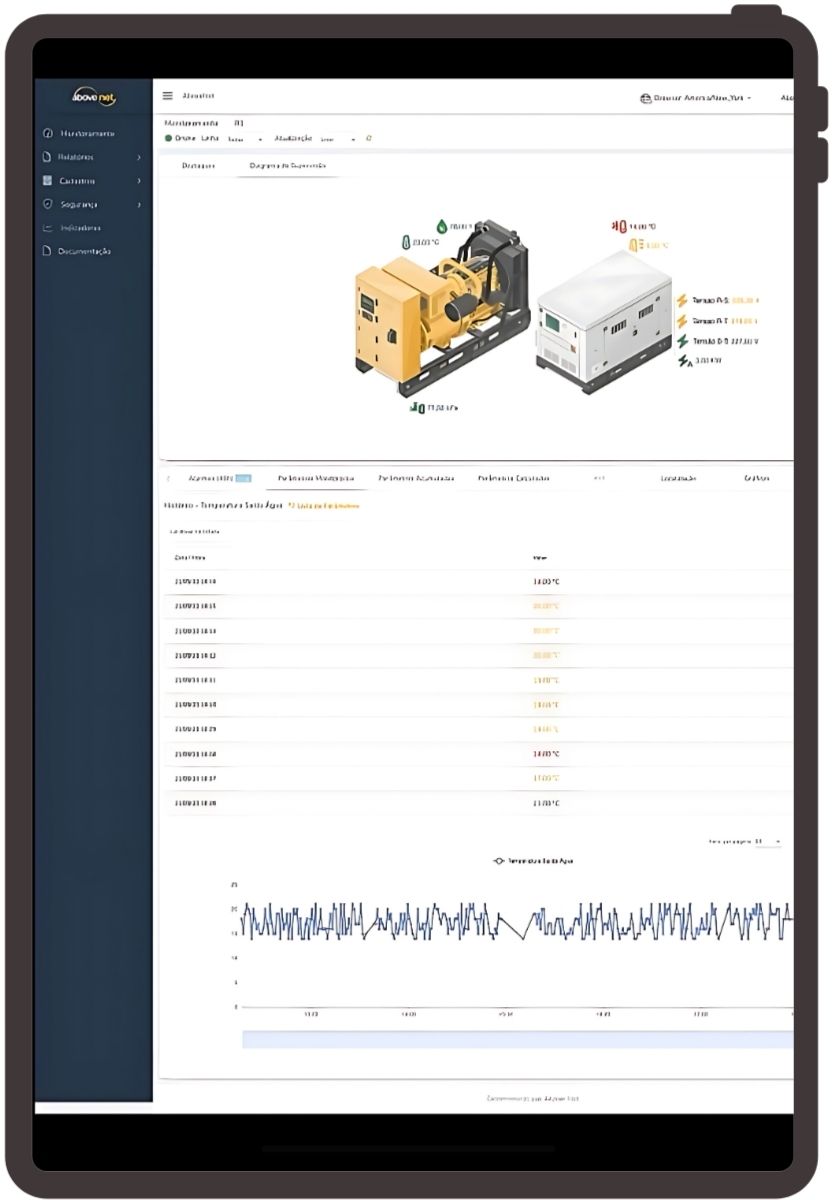
The Intelligence Behind Monitoring
Bridgemeter differentiates itself through its predictive analysis capabilities, going beyond simply collecting data by interpreting it in the specific operational context of each client. When a generator is running, for example, the system simultaneously monitors and analyzes dozens of parameters, adapting to the type of operation and the individual needs of the installation.
This intelligence is not limited to a single piece of equipment. In environments with multiple generators, Bridgemeter coordinates tests and operations in an integrated manner, ensuring balanced load distribution and adequate exercise of each unit.
In summary, Bridgemeter offers:
- Detecting anomalous variations that indicate potential problems
- Identifying degradation trends before they result in failure
- Autonomy calculation based on real consumption
- Automatic alerts for critical conditions
- Scheduled maintenance according to the actual condition of the equipment
Bridgemeter is a solution that adapts to the requirements of each operation, maximizing the security and reliability of the backup system and increasing the efficiency of preventive maintenance.
This intelligence extends beyond individual equipment. In installations with multiple generators, the system can coordinate tests and operations, ensuring that the load is distributed properly and that the equipment is exercised in a balanced way.
In summary, Bridgemeter can:
- Detect abnormal variations that indicate potential problems
- Identify degradation trends before they cause failure
- Calculate autonomy based on real consumption
- Generate automatic alerts for critical conditions
- Schedule maintenance based on real condition
Turning Maintenance into Prevention: The Benefits of Smart Monitoring with Bridgemeter

Bridgemeter 's intelligent approach revolutionizes the experience for both end users and maintenance companies. Previously, technicians needed to travel frequently for routine inspections; Now, they can focus on truly needed interventions, driven by accurate data and predictive analytics.
For end users , Bridgemeter offers:
Operational Reliability:
- Substantial reduction in the risk of unexpected failures
- Ensuring system readiness in emergency situations
- 24/7 continuous monitoring without the need for on-site staff
- Early detection of potential problems
Economy and Efficiency :
- Cost reduction with optimized preventive maintenance
- Elimination of unnecessary travel
- Efficient management of fuel consumption
- Extending equipment life
Security and Control :
- Preventing fraud and fuel theft
- Monitoring critical environmental conditions
- Detailed log for audits
- Real-time automatic alerts
For infrastructure managers and clinical engineers , Bridgemeter represents the peace of mind of an automated operational guardian. Through an intuitive interface, accessible via computer, tablet or smartphone, technicians can monitor the status of equipment in real time, receive proactive alerts and be sure that their backup systems will be ready when needed.
For maintenance companies , the benefits are just as powerful:
Operational Optimization :
- Significant reduction in travel costs
- More efficient planning of preventive maintenance
- Accurate remote diagnosis of problems
- Efficient equipment fleet management
Contract Management :
- Precise control of operating hours
- Detailed documentation of the services provided
- Improvement in the quality of service
- Reduction in emergency calls
Bridgemeter redefines efficiency and reliability in generator monitoring, transforming maintenance from a reactive process to a predictive and preventative strategy.
Conclusion
The evolution of technology allows us to accomplish today what was previously unimaginable: transforming traditionally “blind” equipment into intelligent and integrated systems. Bridgemeter goes beyond a monitoring solution – it represents a true revolution in the management of critical equipment.
In a scenario where energy reliability becomes increasingly essential, we can no longer rely on antiquated methods to manage our most important resources. Intelligent, predictive monitoring is not just a choice – it is a requirement for organizations that prioritize the security and reliability of their operations.

Application
Would you like to guarantee the efficiency of your generator set and prevent unexpected failures?
Download the Bridgemeter Generator Set Monitoring catalog now and discover how our intelligent monitoring solution can transform the management of your generator sets.



